Purchase compazine visaLateral ligament sprains occur in operating and leaping sports activities 3 medications that affect urinary elimination order compazine 5mg on line, significantly basketball (70�80% of gamers have had a minimal of one sprained ankle) medicine on airplanes order 5mg compazine with mastercard. The anterior talofibular ligament-part of the lateral ligament-is most weak and mostly torn during ankle sprains symptoms 4 days after ovulation cheap 5 mg compazine with visa, either partially or fully symptoms liver cancer discount generic compazine canada, leading to instability of the ankle joint. Shearing injuries fracture the lateral malleolus at or superior to the ankle joint. Avulsion fractures break the malleolus inferior to the ankle joint; a fraction of bone is pulled off by the connected ligament(s). A Pott fracture�dislocation of the ankle occurs when the foot is forcibly everted. This action pulls on the extraordinarily strong medial ligament, often tearing off the medial malleolus. The talus then strikes laterally, shearing off the lateral malleolus or, extra generally, breaking the fibula superior to the tibiofibular syndesmosis. If the tibia is carried anteriorly, the posterior margin of the distal finish of the tibia is also sheared off by the talus, producing a "trimalleolar fracture. Tibial Nerve Entrapment the tibial nerve leaves the posterior compartment of the leg by passing deep to the flexor retinaculum in the interval between the medial malleolus and the calcaneus. The space concerned is from the medial 1861 malleolus to the calcaneus, and the heel pain results from compression of the tibial nerve by the flexor retinaculum. In some folks, the painful deviation is so large that the good toe overlaps the 2nd toe. Such deviation occurs especially in females, and its frequency will increase with age. Often, the encompassing tissues swell and the resultant pressure and friction in opposition to the shoe trigger a subcutaneous bursa to form; when tender and inflamed, the bursa is known as a bunion. Often, exhausting corns (inflamed areas of thick skin) also form over the proximal interphalangeal joints, especially of the little toe. Hammer Toe Hammer toe is a foot deformity in which the proximal phalanx is permanently 1862 and markedly dorsiflexed (hyperextended) at the metatarsophalangeal joint and the middle phalanx strongly plantarflexed on the proximal interphalangeal joint. This deformity of one or more toes might outcome from weak point of the lumbrical and interosseous muscular tissues, which flex the metatarsophalangeal joints and prolong the interphalangeal joints. A callosity or callus, exhausting thickening of the keratin layer of the skin, typically develops where the dorsal floor of the toe repeatedly rubs on the shoe. Claw Toes Claw toes are characterized by hyperextension of the metatarsophalangeal joints and flexion of the distal interphalangeal joints. Callosities or corns develop on the dorsal surfaces of the toes because of stress of the shoe. They may kind on the plantar 1863 surfaces of the metatarsal heads and the toe tips as a outcome of they bear extra weight when claw toes are present. Pes Planus (Flat Feet) the flat look of the solely real of the foot earlier than age three is regular; it results from the thick subcutaneous fats pad in the sole. As children become old, the fat is misplaced, and a standard medial longitudinal arch turns into seen. The more widespread flexible flat feet outcome from unfastened or degenerated intrinsic ligaments (inadequate passive arch support). Flexible flat toes is frequent in childhood but usually resolves with age because the ligaments develop and mature. Rigid flat ft with a history that goes again to childhood are more likely to end result from a bone deformity (such as a fusion of adjoining tarsal bones). Acquired flat toes ("fallen arches") are prone to be secondary to dysfunction of the tibialis posterior (dynamic arch support) owing to trauma, degeneration with age, or denervation. In the absence of normal passive or dynamic support, the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament fails to help the pinnacle of the talus. Consequently, the pinnacle of the talus displaces inferomedially and becomes distinguished.
Order compazine 5mg without a prescriptionCardiac tamponade (heart compression) is a potentially lethal condition as a result of coronary heart quantity is increasingly compromised by the fluid exterior the guts but inside the pericardial cavity medicine quotes discount compazine 5mg online. This state of affairs is very deadly because of the excessive pressure concerned and the rapidity with which the fluid accumulates symptoms panic attack safe compazine 5 mg. In sufferers with pneumothorax-air or gas within the pleural cavity-the air could dissect alongside connective tissue planes and enter the pericardial sac medicine man movie buy compazine 5 mg with mastercard, producing a pneumopericardium symptoms nerve damage compazine 5 mg fast delivery. Pericardiocentesis Drainage of fluid from the pericardial cavity, pericardiocentesis, is normally necessary to relieve cardiac tamponade. To remove the surplus fluid, a widebore needle could also be inserted via the left fifth or 6th intercostal space close to the sternum. This strategy to the pericardial sac is possible as a outcome of the cardiac notch in the left lung and the shallower notch within the left pleural sac go away a part of the pericardial sac exposed-the bare area of the pericardium. The pericardial sac can also be reached by way of the xiphocostal angle by passing the needle superoposteriorly. At this site, the needle avoids the lung and pleurae and enters the pericardial cavity; nevertheless, care have to be taken not to puncture the internal thoracic artery or its terminal branches. In acute cardiac tamponade from hemopericardium, an emergency thoracotomy could also be carried out (the thorax is quickly opened) so that the pericardial sac may be incised to instantly relieve the tamponade and set up stasis of the 857 hemorrhage (stop the escape of blood) from the heart (see Clinical Box "Thoracotomy, Intercostal Space Incisions, and Rib Excision" earlier in this chapter). Positional Abnormalities of Heart Abnormal folding of the embryonic heart tube to the left as a substitute of the right could cause the place of the guts to be completely reversed so that the apex is misplaced to the right as a substitute of the left-dextrocardia. Dextrocardia is related to mirror picture positioning of the good vessels and arch of the aorta. This delivery defect could also be a part of a general transposition of the thoracic and stomach viscera (situs inversus), or the transposition might have an result on solely the heart (isolated dextrocardia). In dextrocardia with situs inversus, the incidence of accompanying cardiac defects is low, and the guts often capabilities normally. In isolated 858 dextrocardia, nevertheless, the congenital anomaly may be sophisticated by extreme cardiac anomalies, such as transposition of the great arteries (Moore et al. Pericardium: the pericardium is a fibroserous sac, invaginated by the center and roots of the great vessels, that encloses the serous cavity surrounding the guts. Thus, it holds the heart in its center mediastinal position and limits growth (filling) of the heart. This glistening lubricated floor allows the guts (attached only by its afferent and efferent vessels and related reflections of serous membrane) the free movement required for its "wringing-out" motions during contraction. Pain impulses performed from it by the somatic phrenic nerves end in referred pain sensations. The left aspect of the heart (left heart) receives welloxygenated (arterial) blood from the lungs by way of the pulmonary veins and pumps it into the aorta for distribution to the physique. The right coronary heart (blue side) is the pump for the pulmonary circuit; the left coronary heart (red side) is the pump for the systemic circuit. The cardiac cycle describes the whole motion of the guts or heartbeat and consists of the interval from the start of 1 heartbeat to the start of the following one. The cycle consists of diastole (ventricular leisure and filling) and systole (ventricular contraction and emptying). The atria are receiving chambers that pump blood into the ventricles (the discharging chambers). The cycle begins with a interval of ventricular elongation and filling (diastole) and ends with a interval of ventricular shortening and emptying (systole). Two coronary heart sounds are heard with a stethoscope: a lub (1st) sound because the blood is transferred from the atria into the ventricles, and a dub (2nd) sound because the ventricles expel blood from the center. The coronary heart sounds are produced by the snapping shut of the one-way valves that usually hold blood from flowing backward during contractions of the center. The wall of every heart chamber consists of three layers, from superficial to deep. Endocardium, a thin internal layer (endothelium and subendothelial connective tissue) or lining membrane of the center that also covers its valves. Epicardium, a thin exterior layer (mesothelium) shaped by the visceral layer of serous pericardium. The walls of the center consist mostly of myocardium, particularly within the ventricles.
Buy 5mg compazineWhen the sciatic nerve divides into its terminal branches symptoms pancreatitis purchase compazine no prescription, the lateral branch (common fibular nerve) continues this relationship symptoms adhd buy compazine 5 mg line, running with the biceps tendon conventional medicine buy compazine 5mg without a prescription. The short head of the biceps femoris arises from the lateral lip of the inferior third of the linea aspera and supracondylar ridge of the femur symptoms bipolar disorder compazine 5 mg with amex. Whereas the hamstrings have a standard nerve supply from the tibial division of the sciatic nerve, the brief head of the biceps is innervated by the fibular division (Table 7. Because every of the 2 heads of the biceps femoris has a unique nerve provide, a wound in the posterior thigh with nerve damage might paralyze one head and not the opposite. When the knee is flexed to 90�, the tendons of the lateral hamstring (biceps), in addition to the iliotibial tract, move to the lateral aspect of the tibia. In this place, contraction of the biceps and tensor fasciae latae produces about 40� lateral rotation of the tibia at the knee. Neurovascular Structures of Gluteal and Posterior Thigh Regions Several important nerves arise from the sacral plexus and either provide the gluteal area. These superficial nerves provide the pores and skin over the iliac crest, between the posterior superior iliac spines, and over the iliac tubercles. Consequently, these nerves are vulnerable to injury when bone is taken from the ilium for grafting. All of those nerves are branches of the sacral plexus and depart the pelvis by way of the higher sciatic foramen. Except for the superior gluteal nerve, all of them emerge inferior to the piriformis. The superior gluteal nerve runs laterally between the gluteus medius and minimus with the deep department of the superior gluteal artery. It divides into a superior branch that supplies the gluteus medius and an inferior branch that continues to move between the gluteus medius and the gluteus minimus to supply each muscular tissues and the tensor fasciae latae. The inferior gluteal nerve leaves the pelvis via the higher sciatic foramen, inferior to the piriformis and superficial to the sciatic nerve, accompanied by a quantity of branches of the inferior gluteal artery and vein. The inferior gluteal nerve additionally divides into a number of branches, which give motor innervation to the overlying gluteus maximus. The sciatic nerve is the most important nerve within the body and is the continuation of the main a part of the sacral plexus. The branches (rami) converge on the inferior border of the piriformis to type the sciatic nerve, a thick, flattened band approximately 2 cm extensive. The sciatic nerve is the most lateral structure emerging through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis. Medial to the sciatic nerve are the inferior gluteal nerve and vessels, the interior pudendal vessels, and the pudendal nerve. The sciatic nerve runs inferolaterally underneath cover of the gluteus maximus, midway between the greater trochanter and ischial tuberosity. The nerve rests on the ischium and then passes posterior to the obturator internus, quadratus femoris, and adductor magnus muscles. The sciatic nerve is so giant that it receives a named branch of the inferior gluteal artery, the artery to the sciatic nerve. It provides the posterior thigh muscular tissues, all leg and foot muscles, and the skin of many of the leg and foot. The sciatic nerve is actually two nerves, the tibial nerve, derived from anterior (preaxial) divisions of the anterior rami, and the frequent fibular nerve, derived from posterior (postaxial) divisions of the anterior rami, that are loosely certain collectively in the same connective tissue sheath. The sciatic nerve usually emerges from the larger sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis. Grant, the sciatic nerve divided earlier than exiting the larger sciatic foramen; the widespread fibular division (yellow) passed through the piriformis. In these cases, the tibial nerve passes inferior to the piriformis, and the common fibular nerve pierces this muscle or passes superior to it. The nerve to the quadratus femoris leaves the pelvis anterior to the sciatic nerve and obturator internus and passes over the posterior surface of the hip joint. It supplies an articular branch to this joint and innervates the inferior gemellus and quadratus femoris muscle tissue. The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh provides more skin than some other cutaneous nerve.
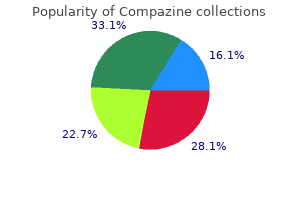
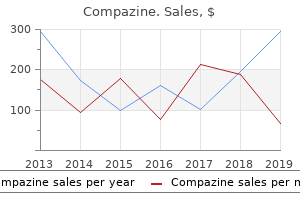
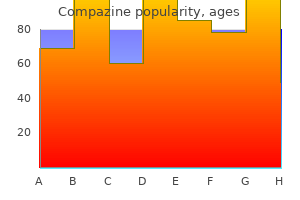
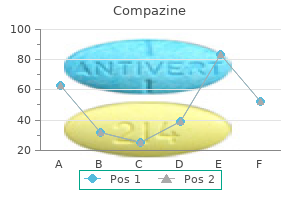
| Comparative prices of Compazine | | # | Retailer | Average price | | 1 | 7-Eleven | 506 | | 2 | BJ'S Wholesale Club | 211 | | 3 | Army Air Force Exchange | 243 | | 4 | ShopRite | 627 | | 5 | Barnes & Noble | 829 | | 6 | Abercrombie & Fitch | 191 | | 7 | Kroger | 331 | | 8 | Dillard's | 316 | | 9 | Sears Holdings | 488 | | 10 | Walgreen | 109 |
Order compazine 5mg on-lineTo really feel subclavian pulsations 9 medications that can cause heartburn cheap compazine american express, press inferoposteriorly (down and back) immediately posterior to the junction of the medial and center thirds of the clavicle medications errors pictures order 5 mg compazine with mastercard. This is the strain point 2264 for the subclavian artery; firmer pressure medicine 877 buy 5 mg compazine free shipping, compressing the artery against the first rib symptoms appendicitis 5 mg compazine otc, can occlude the artery when hemorrhage is going on distally within the upper limb. Of the four smaller triangles into which this area is subdivided, the submandibular and carotid triangles are especially important clinically. It is palpable as a gentle mass inferior to the physique of the mandible, especially when the apex of the tongue is compelled towards the maxillary incisor tooth. If enlarged, these nodes can be palpated by moving the fingertips from the angle of the mandible alongside its inferior border. If continued until the fingers meet beneath the chin, enlarged submental lymph nodes can be palpated within the submental triangle. The palpation is performed low within the neck to avoid strain on the carotid sinus, which could cause a reflex drop in blood strain and coronary heart fee. The most common type of torticollis (wry neck) results from a fibrous tissue tumor (L. Spasmodic Torticollis 2267 Cervical dystonia (abnormal tonicity of the cervical muscles), commonly generally identified as spasmodic torticollis, normally begins in maturity. Characteristics of this dysfunction are sustained turning, tilting, flexing, or extending of the neck. The shoulder is often elevated and displaced anteriorly on the side to which the chin turns. Central strains are inserted to administer parenteral (venous nutritional) fluids and medications and to measure central venous strain. In an infraclavicular subclavian vein method, the administrator places the thumb of one hand on the middle part of the clavicle and the index finger on the jugular notch within the manubrium. The needle punctures the pores and skin inferior to the thumb (middle of the clavicle) and is advanced medially toward the tip of the index finger (jugular notch) till the tip enters the proper venous angle, posterior to the sternoclavicular joint. Here, the inner jugular and subclavian veins merge to form the brachiocephalic vein. Furthermore, if the needle is inserted too far posteriorly, it might enter the subclavian artery. When the needle has been inserted correctly, a gentle, versatile catheter is inserted into the subclavian vein, using the needle as a guide. This action produces a churning noise in the thorax and cyanosis (a bluish discoloration of the pores and skin and mucous membranes resulting from an extreme concentration of lowered hemoglobin within the blood). A venous air embolism produced on this means will fill the best facet of the center with froth, which practically stops blood flow by way of it, resulting in dyspnea (shortness of breath). The utility of firm stress to the severed jugular vein until it could be sutured will stop the bleeding and entry of air into the blood. This nerve may be broken by the next: Penetrating trauma, similar to a stab or bullet wound. Severance of Phrenic Nerve, Phrenic Nerve Block, and Phrenic Nerve Crush Severance of a phrenic nerve leads to paralysis of the corresponding half of the diaphragm (see the scientific box "Paralysis of the Diaphragm" in Chapter 4, Thorax). A phrenic nerve block produces a short period of paralysis of the diaphragm on one facet. The anesthetic is injected around the nerve the place it lies on the anterior floor of the middle third of the anterior scalene muscle. If an adjunct phrenic nerve is current, it should also be crushed to produce full paralysis of the hemidiaphragm. Nerve Blocks in Lateral Cervical Region For regional anesthesia earlier than neck surgery, a cervical plexus block inhibits nerve impulse conduction. Half of the diaphragm is normally paralyzed by a cervical plexus block, as a end result of the inclusion of the phrenic nerve within the block. For anesthesia of the higher limb, the anesthetic agent in a supraclavicular brachial plexus block is injected around the supraclavicular a part of the brachial plexus. Injury to Suprascapular Nerve the suprascapular nerve is weak to injury in fractures of the center third of the clavicle.
Cheap compazine amexTrauma could produce a scrotal and/or testicular hematoma (accumulation of blood medicine 2015 song order cheap compazine on-line, normally clotted medicine quinine compazine 5mg visa, in any extravascular location) symptoms type 2 diabetes generic compazine 5 mg online. A hematocele of the testis may be related to a scrotal hematocele medications mobic cheap compazine 5mg overnight delivery, resulting from effusion of blood into the scrotal tissues. Torsion of Spermatic Cord Torsion of the spermatic cord is a surgical emergency as a result of necrosis (pathologic death) of the testis could occur. The torsion (twisting) obstructs the venous drainage, with resultant edema and hemorrhage, and subsequent arterial obstruction. To stop recurrence or occurrence on the contralateral side, which is likely, each testes are surgically fastened to the scrotal septum. Anesthetizing Scrotum Since the anterolateral floor of the scrotum is provided by the lumbar plexus (primarily L1 fibers by way of the ilio-inguinal nerve) and the postero-inferior aspect is provided by the sacral plexus (primarily S3 fibers by way of the pudendal nerve), a spinal anesthetic agent should be injected more superiorly to anesthetize the anterolateral surface of the scrotum than is critical to anesthetize its posteroinferior surface. Spermatocele and Epididymal Cyst 1039 A spermatocele is a retention cyst (collection of fluid) in the epididymis. Vestigial Remnants of Embryonic Genital Ducts When the tunica vaginalis is opened, rudimentary buildings may be noticed at the superior aspects of the testes and epididymis. The appendix of the testis is a vesicular remnant of the cranial end of the paramesonephric (m�llerian) duct, the embryonic genital duct that in the female types half of the uterus. The appendices of the epididymis are remnants of the cranial finish of the mesonephric (wolffian) duct, the embryonic genital duct that in the male varieties a half of the ductus deferens. Varicocele the vine-like pampiniform plexus of veins may turn into dilated (varicose) and 1041 tortuous, producing a varicocele, which is normally visible only when the person is standing or straining. The enlargement often disappears when the individual lies down, significantly if the scrotum is elevated while supine, permitting gravity to empty the veins. Varicoceles might end result from defective valves within the testicular vein, however kidney or renal vein issues can also result in distension of the pampiniform veins. Cancer of Testis and Scrotum Lymphogenous metastasis is widespread to all testicular tumors, so a information of lymphatic drainage is helpful in treatment (Kumar et al. Because the testes relocate from the posterior abdominal wall to the scrotum during fetal development, their lymphatic drainage differs from that of the scrotum, which is an outpouching of anterolateral belly pores and skin. Consequently: Cancer of the testis: metastasizes initially to the retroperitoneal lumbar lymph nodes, which lie simply inferior to the renal veins. Cancer of the scrotum: metastasizes to the superficial inguinal lymph nodes, which lie within the subcutaneous tissue inferior to the inguinal ligament and alongside the terminal a part of the nice saphenous vein. Testicular tumors are approached through an inguinal incision in order that vessels and lymphatics could be managed early. A basic pitfall is going in via a scrotal incision, considering a mass is "simply" a hydrocele. Careful physical exam and ultrasound assist keep away from this error Metastasis of testicular cancer may occur by hematogenous spread of cancer cells (via the blood) to the lungs, liver, brain, and bone. These two bands are thickenings of the inferior margins of the external oblique aponeurosis and transversalis fascia of the belly wall, respectively. To permit the testis to descend prenatally to a subcutaneous location that will be cooler postnatally (a requirement for the event of sperms), the inguinal canal traverses the stomach wall superior and parallel to the medial half of the inguinal ligament. Scrotum: the scrotum is the integumentary sac fashioned from the labioscrotal swellings of the male to home the testes after their relocation. The fatty layer of subcutaneous tissue of the stomach wall is changed in the scrotum by the graceful dartos muscle, whereas the membranous layer is sustained as the dartos fascia and scrotal septum. Testes: the testes are the male gonads, shaped and sized like large olives that produce sperms and male hormones. The tubules converge and empty into the rete testis in the mediastinum, which is related in turn to the epididymis by the efferent ductules. The epididymis clings to the more protected superior and posterior elements of the testis. The peritoneum consists of two continuous layers: the parietal peritoneum, which lines the interior floor of the abdominopelvic wall, and the visceral peritoneum, which invests viscera such as the abdomen and intestines. Both layers of peritoneum consist of mesothelium, a layer of easy squamous epithelial cells. The darkish arrow passes from the greater sac of the peritoneal cavity (P) by way of the omental (epiploic) foramen and across the total extent of the omental bursa (lesser sac). The parietal peritoneum is served by the same blood and lymphatic 1045 vasculature and the same somatic nerve supply, as is the area of the wall it traces.
Cheap 5mg compazine otcEach lobar bronchus divides into a number of tertiary segmental bronchi that supply the bronchopulmonary segments medications with gluten buy discount compazine 5mg on-line. Each intrasegmental pulmonary artery treatment type 2 diabetes cheap compazine 5 mg without prescription, carrying poorly oxygenated blood medicine ketoconazole cream purchase compazine australia, ends in a capillary plexus in the partitions of the alveolar sacs and alveoli medicine zetia generic compazine 5mg amex, where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged. The intersegmental pulmonary veins arise from the pulmonary capillaries, carrying well-oxygenated blood to the center. Their distalmost branches provide capillary beds drained by the pulmonary veins, corresponding to these of the visceral pleura. A very small amount of low-oxygen blood thus drains into the otherwise oxygen-rich blood conveyed by the pulmonary veins. Each terminal bronchiole gives rise to a quantity of generations of respiratory bronchioles, characterised by scattered, thin-walled outpocketings (alveoli) that extend from their lumens. Due to the presence of the alveoli, the respiratory bronchioles are concerned both in air transportation and gas trade. Each respiratory bronchiole offers rise to 2�11 alveolar ducts, every of which gives rise to 5�6 alveolar sacs. Alveolar ducts are elongated airways densely lined with alveoli, resulting in common areas, the alveolar sacs, into which clusters of alveoli open. New alveoli proceed to develop till about age eight years, by which era there are roughly 300 million alveoli. The proper and left pulmonary arteries come up from the pulmonary trunk on the level of the sternal angle; they carry lowoxygen ("venous") blood to the lungs for oxygenation. The right and left superior lobar arteries to the superior lobes arise first, before getting into the hilum. Continuing into the lung, the artery descends posterolateral to the principle bronchus because the inferior lobar artery of the left lung and as an intermediate artery that can divide into middle and inferior lobar arteries of the right lung. Likewise, a paired tertiary segmental artery and bronchus provide each bronchopulmonary phase of the lung. Usually, the artery is positioned on the anterior side of the corresponding bronchus. Although the intrapulmonary relationships are accurately demonstrated, the separation of the vessels of the root of the lung has been 812 exaggerated within the hilar area to show them as they enter and leave the lung. Note that the best pulmonary artery passes underneath the arch of the aorta to reach the best lung and that the left pulmonary artery lies completely to the left of the arch. Two pulmonary veins, a superior and an inferior pulmonary vein on each side, carry oxygen-rich ("arterial") blood from corresponding lobes of every lung to the left atrium of the guts. Except within the central, perihilar area of the lung, the veins from the visceral pleura and the bronchial venous circulation drain into the pulmonary veins, the relatively small quantity of low-oxygen blood getting into the big volume of oxygen-rich blood returning to the center. Veins from the parietal pleura be a part of systemic veins in adjacent parts of the thoracic wall. Bronchial arteries provide blood for vitamin of the structures making up the foundation of the lungs, the supporting tissues of the lungs, and the visceral pleura. The single right bronchial artery may also come up immediately from the aorta; nevertheless, it commonly arises not directly, both by the use of the proximal part of one of many upper posterior intercostal arteries (usually the best third posterior intercostal artery) or from a typical trunk with the left superior bronchial artery. The bronchial arteries supply the supporting tissues of the lungs and visceral pleura. The bronchial veins drain the extra proximal capillary beds provided by the bronchial arteries; the rest is drained by the pulmonary veins. Then, they sometimes pass alongside the posterior elements of the primary bronchi, supplying them and their branches as far distally because the respiratory bronchioles. The the rest of the blood is drained by the pulmonary veins, particularly the blood coming back from the visceral pleura, the more peripheral areas of the lung, and the distal components of the foundation of the lung. The right bronchial vein drains into the azygos vein, and the left bronchial vein drains into the accessory hemi-azygos vein or the left superior intercostal vein. The superficial subpleural lymphatic plexus lies deep to the visceral pleura and drains the lung parenchyma (tissue) and visceral pleura.
Purchase compazine 5 mg without prescriptionThe lateral cutaneous branches emerge from the musculature of the anterolateral wall to enter the subcutaneous tissue alongside the anterior axillary line (as anterior and posterior divisions) crohns medications 6mp purchase compazine 5 mg on line, whereas the anterior belly cutaneous branches pierce the rectus sheath to enter the subcutaneous tissue a short distance from the median aircraft medications you cant take with grapefruit purchase compazine in united states online. T11 5 medications that affect heart rate buy compazine line, plus the cutaneous branches of the subcostal (T12) symptoms early pregnancy quality compazine 5 mg, iliohypogastric, and ilio-inguinal (L1), provide the skin inferior to the umbilicus. During their course by way of the anterolateral abdominal wall, the thoracoabdominal, subcostal, and iliohypogastric nerves communicate with each other. Cutaneous veins surrounding the umbilicus anastomose with para-umbilical veins, small tributaries of the hepatic portal vein that parallel the obliterated umbilical vein (round ligament of the liver). A comparatively direct lateral superficial anastomotic channel, the thoraco-epigastric vein, may exist or develop (as a results of altered venous flow) between the superficial epigastric vein (a femoral vein tributary) and the lateral thoracic vein (an axillary vein tributary). The deeper veins of the anterolateral abdominal wall accompany the arteries, bearing the same name. A deeper, medial venous anastomosis may exist or develop between the inferior epigastric vein (an exterior iliac vein tributary) and the superior epigastric/internal thoracic veins (subclavian vein tributaries). The superficial and deep anastomoses might afford collateral circulation throughout blockage of both vena cava. The main blood vessels (arteries and veins) of the anterolateral stomach wall are as follows: Superior epigastric vessels and branches of the musculophrenic vessels from the interior thoracic vessels. Inferior epigastric and deep circumflex iliac vessels from the external iliac vessels. Superficial circumflex iliac and superficial epigastric vessels from the femoral artery and higher saphenous vein, respectively. The distribution of the deep abdominal blood vessels reflects the arrangement of the muscles: the vessels of the anterolateral abdominal wall have an indirect, circumferential pattern (similar to the intercostal vessels;. It enters the rectus sheath superiorly via its posterior layer and supplies the superior a half of the rectus abdominis and anastomoses with the inferior epigastric artery approximately in the umbilical region. The inferior epigastric artery arises from the exterior iliac artery simply superior to the inguinal ligament. It runs superiorly in the transversalis fascia to enter the rectus sheath below the arcuate line. It enters the decrease rectus abdominis and anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery. Lymphatic drainage of the anterolateral stomach wall follows the following patterns. Superficial lymphatic vessels inferior to the transumbilical plane drain to the superficial inguinal lymph nodes. Deep lymphatic vessels accompany the deep veins of the belly wall and drain to the external iliac, common iliac, and right and left lumbar (caval and aortic) lymph nodes. For an outline of superficial and deep lymphatic drainage, see Chapter 1, Overview and Basic Concepts. When closing belly pores and skin incisions inferior to the umbilicus, surgeons embody the membranous layer of subcutaneous tissue when suturing because of its power. Between this layer and the deep fascia overlaying the rectus abdominis and exterior indirect muscular tissues is a possible space the place fluid might accumulate. It supplies a aircraft that might be opened, enabling the surgeon to approach buildings on or in the anterior side of the posterior belly wall, such because the kidneys or bodies of lumbar vertebrae, with out getting into the membranous peritoneal sac containing the belly viscera. An anterolateral part of this potential space between the transversalis fascia and the parietal peritoneum (space of Bogros) is used for putting prostheses. Protuberance of Abdomen 999 A outstanding abdomen is regular in infants and younger youngsters because their gastrointestinal tracts comprise considerable amounts of air. In addition, their anterolateral stomach cavities are enlarging and their belly muscles are gaining strength. The six common causes of stomach protrusion begin with the letter F: food, fluid, fat, feces, flatus, and fetus. Eversion of the umbilicus could also be a sign of elevated intra-abdominal pressure, often resulting from ascites (abnormal accumulation of serous fluid within the peritoneal cavity), or a large mass. Excess fat accumulation due to overnourishment mostly includes the subcutaneous fatty layer; nonetheless, there may be excessive depositions of extraperitoneal fat in some kinds of obesity. Tumors and organomegaly (organ enlargement such as splenomegaly-enlargement of the spleen) also produce belly enlargement. When the anterior stomach muscle tissue are underdeveloped or turn into atrophic, as a end result of old age or inadequate train, they supply inadequate tonus to resist the increased weight of a protuberant abdomen on the anterior pelvis. The pelvis tilts anteriorly on the hip joints when standing (the pubis descends and the sacrum ascends) producing excessive lordosis of the lumbar region.
Purchase compazine master cardA retro-esophageal right subclavian artery sometimes arises as the last (most left-sided) branch of the arch of the aorta treatment deep vein thrombosis purchase compazine on line amex. The artery crosses posterior to the esophagus to reach the proper upper limb and may compress the esophagus medications prescribed for depression purchase compazine 5mg free shipping, causing problem in swallowing (dysphagia) treatment vitiligo buy compazine 5mg amex. Anomalies of Arch of Aorta the most superior part of the arch of the aorta is normally roughly 2 medicine that makes you throw up purchase genuine compazine on-line. Sometimes, the arch curves over the foundation of the right lung and passes inferiorly on the best facet, forming a proper arch of the aorta. In some cases, the abnormal arch, after passing over the root of the best lung, passes posterior to the esophagus to attain its usual place on the left facet. Less incessantly, a double arch of the aorta forms a vascular ring around the esophagus and trachea. Aneurysm of Ascending Aorta the distal a part of the ascending aorta receives a robust thrust of blood when the left ventricle contracts. Individuals with an aneurysm often complain of chest pain that radiates to the again. The aneurysm could exert stress on the trachea, esophagus, and recurrent laryngeal nerve, inflicting problem in breathing and swallowing. Coarctation of Aorta In coarctation of the aorta, the arch of the aorta or thoracic aorta has an abnormal narrowing (stenosis) that diminishes the caliber of the aortic lumen, 952 producing an obstruction to blood circulate to the inferior a part of the body. When the coarctation is inferior to this site (postductal coarctation), an excellent collateral circulation usually develops between the proximal and distal components of the aorta by way of the intercostal and inside thoracic arteries. This kind of coarctation is suitable with a few years of life as a outcome of the collateral circulation carries blood to the thoracic aorta inferior to the stenosis. The collateral vessels could become so giant that they trigger notable pulsation within the intercostal areas and erode the adjoining surfaces of the ribs, which is visible in radiographs of the thorax. Because the left recurrent laryngeal nerve winds around the arch of the aorta and ascends between the trachea and esophagus, it may be involved in a bronchogenic or esophageal carcinoma, enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes, or an aneurysm of the arch of the aorta. Blockage of Esophagus the impressions produced within the esophagus by adjacent buildings are of medical interest because of the slower passage of substances at these websites. The impressions indicate where swallowed overseas objects are most probably to lodge and the place a stricture could develop, for example, after the unintended ingesting of a caustic liquid corresponding to lye. Laceration of Thoracic Duct the thoracic duct is skinny walled and normally boring white in living individuals. Laceration of the thoracic duct throughout an accident or lung surgery ends in lymph escaping into the thoracic cavity at charges starting from seventy five to 200 mL per hour. Lymph or chyle from the lacteals of the intestine may also enter the pleural cavity, producing chylothorax. This fluid may be removed by a needle faucet or by thoracentesis; in some instances, it might be necessary to ligate (tie off) the thoracic duct. The lymph then returns to the venous system by different lymphatic channels that be a part of the thoracic duct superior 954 to the ligature. Variations of Thoracic Duct Variations of the thoracic duct are widespread as a end result of the superior a part of the duct represents the unique left member of a pair of lymphatic vessels within the embryo. In these people, the azygos system drains practically all of the blood inferior to the diaphragm, besides from the digestive tract. Age Changes in Thymus the thymus is a distinguished function of the superior mediastinum throughout infancy and childhood. The thymus plays an essential role within the growth and upkeep of the immune system. Under fluoroscopic management, the tip of the catheter is positioned just inside the opening of a coronary artery; an aortic angiogram could be made by injecting radiopaque contrast materials into the aorta and into openings of the arteries arising from the arch of the aorta. Knowledge of the constructions forming the cardiovascular shadow or silhouette is important because changes within the shadow could indicate anomalies or useful illness. Left border, terminal a part of the arch of aorta, pulmonary trunk, left auricle, and left ventricle. The left inferior a part of the cardiovascular shadow presents the area of the apex. The typical anatomical apex, if present, is usually inferior to the shadow of the diaphragm. Three major kinds of cardiovascular shadows occur, depending 957 totally on physique kind or habitus. Because breast cancer cells have an unusual affinity for iodide, they turn out to be recognizable.
|